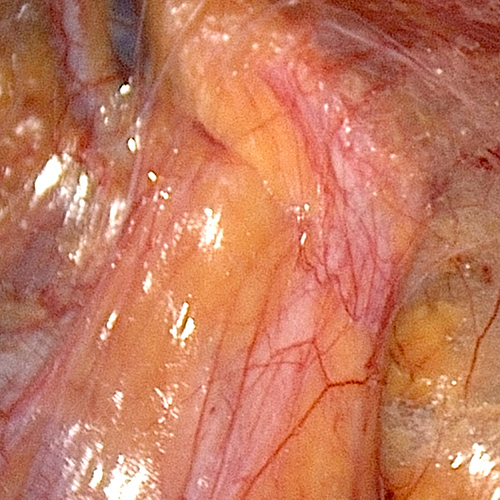
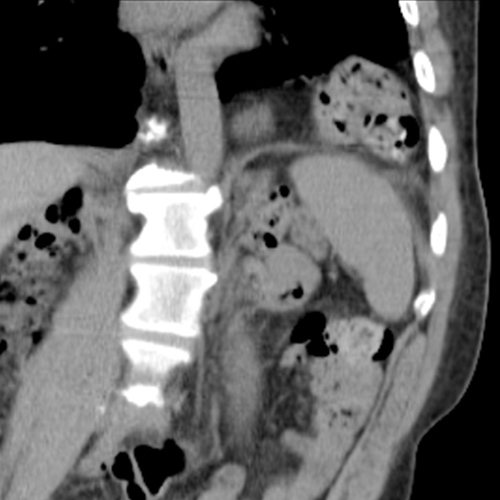
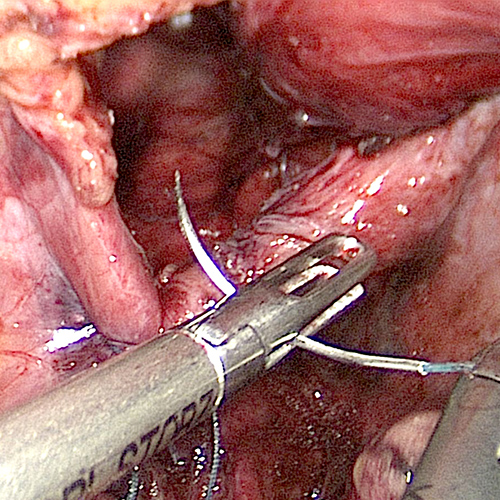
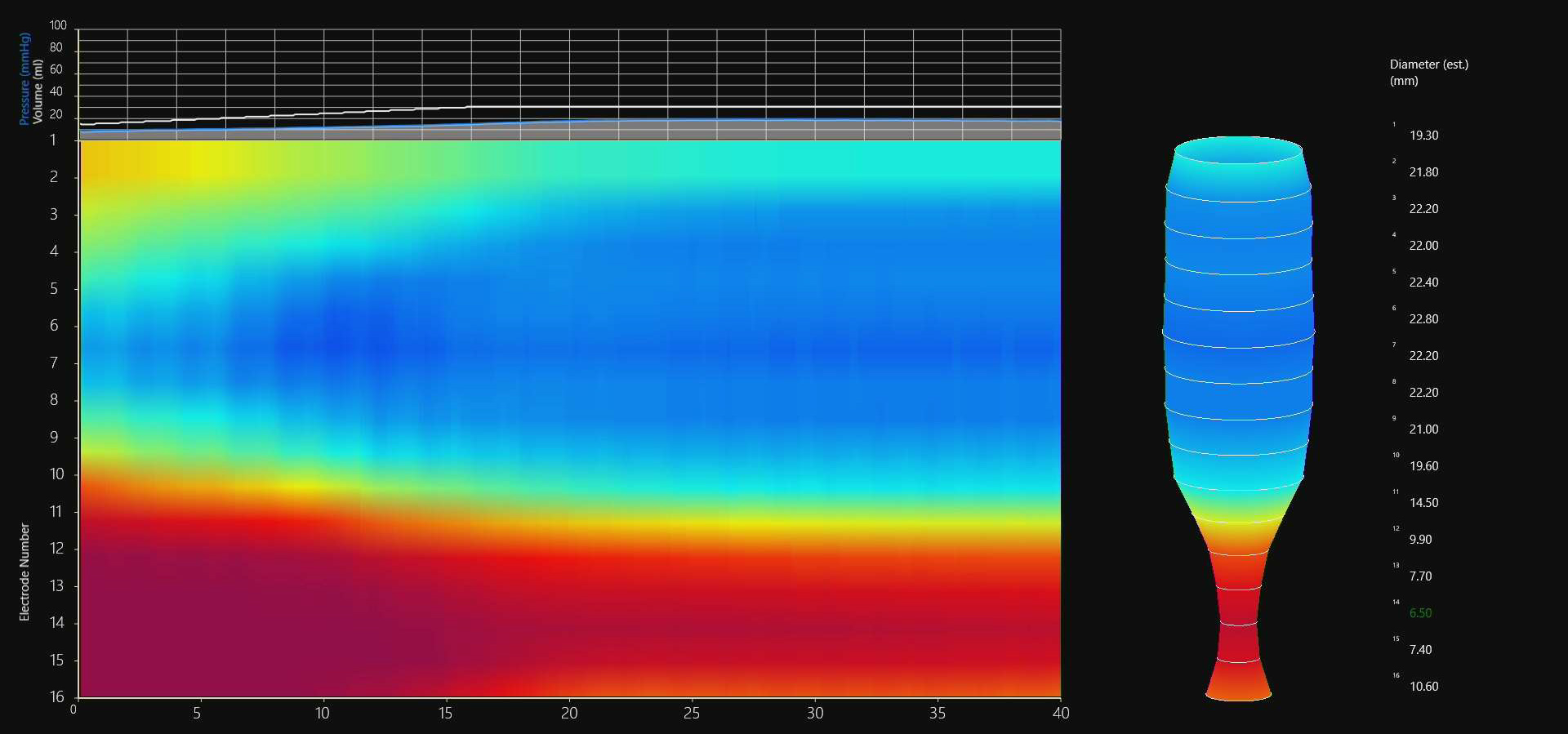
A hernia is referred to as the protrusion of a part of an organ or a tissue from its normal place to some other cavity. Hernia in the abdomen occurs when a piece of intestine or its lining, also called the omentum, protrudes through a weak area present in the abdominal wall. Hernias of the groin (inguinal hernia) and of the diaphragm (hiatal hernia) are some of the common hernias. Hernias may be congenital (when present at birth) or acquired (develop during the lifetime). Umbilical hernia is also a common form of hernia that occurs around the belly button. The abdominal hernias occur as a result of increased pressure in the abdominal cavity that causes stress at the weak points of the abdominal wall leading to protrusion of the abdominal contents. Pressure in the abdominal cavity may increase due to chronic cough, ascites (accumulation of fluid in the abdominal cavity) or peritoneal dialysis (a procedure used to treat kidney failure). Abdominal pressure may also increase during pregnancy and due to excess weight around the abdomen. Lifting excess weight and straining while urinating and passing stool can also increase the pressure in the abdominal cavity.