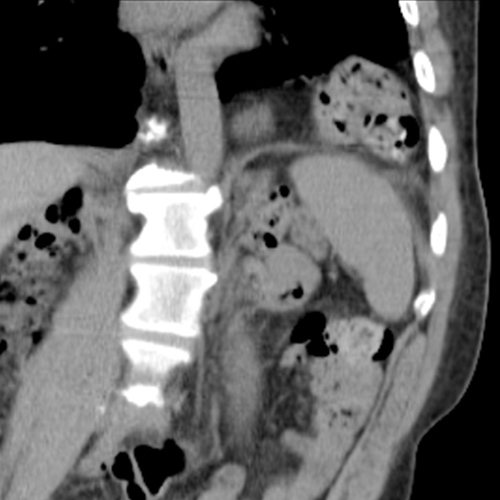
An accumulation of fluid in an organ or a tissue often occurring after surgery or in some cases after an injury such as trauma by a blunt object. Seroma is formed when the fluid, referred to as serum leaks from the damaged blood vessels and lymphatic vessels. The fluid present in a seroma is normally clear. Seroma can form after different types of surgical procedures, especially extensive surgeries or those in which significant tissue disruption occurs. For instance, seroma occurs after hernia repair surgery, plastic surgeries such as breast augmentation surgery or breast reconstruction surgery, tummy tuck surgery, and breast cancer surgery. Seroma formation increases the risk of infection and breakdown of the surgical site. Resolution of small seromas often occurs spontaneously. Aspiration or fluid removal with a needle is often required for large seromas. Infection may occur in a seroma and antibiotics and in some cases surgery may be required to treat them.