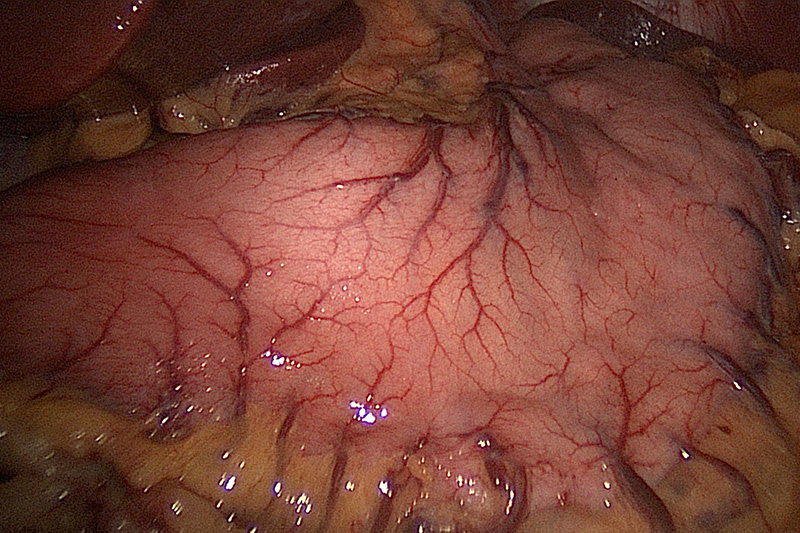
Gastritis is characterized by inflammation or swelling of the gastric mucosa (lining of stomach). It can be classified as acute gastritis (which lasts for a short duration) and chronic gastritis (which may be present for many months or years). There are multiple causes of gastritis. The common ones are drugs such as ibuprofen, aspirin or naproxen, alcohol abuse, and stomach infection by Helicobacter pylori bacterium. Gastritis may also be caused due to certain less common causes including autoimmune disorders, bile reflux, and abuse of cocaine, drinking corrosive or caustic products, stress, and infection with virus such as herpes simplex or cytomegalovirus. Gastritis may not cause any major symptoms in many patients. However, it may cause symptoms of decreased appetite, nausea, vomiting, and pain in the upper abdomen. Vomiting of blood, or black stools may occur in cases where bleeding is occurring from the stomach lining. Treatment depends on the cause and may include antacids, H2 antagonist and proton pump inhibitors.