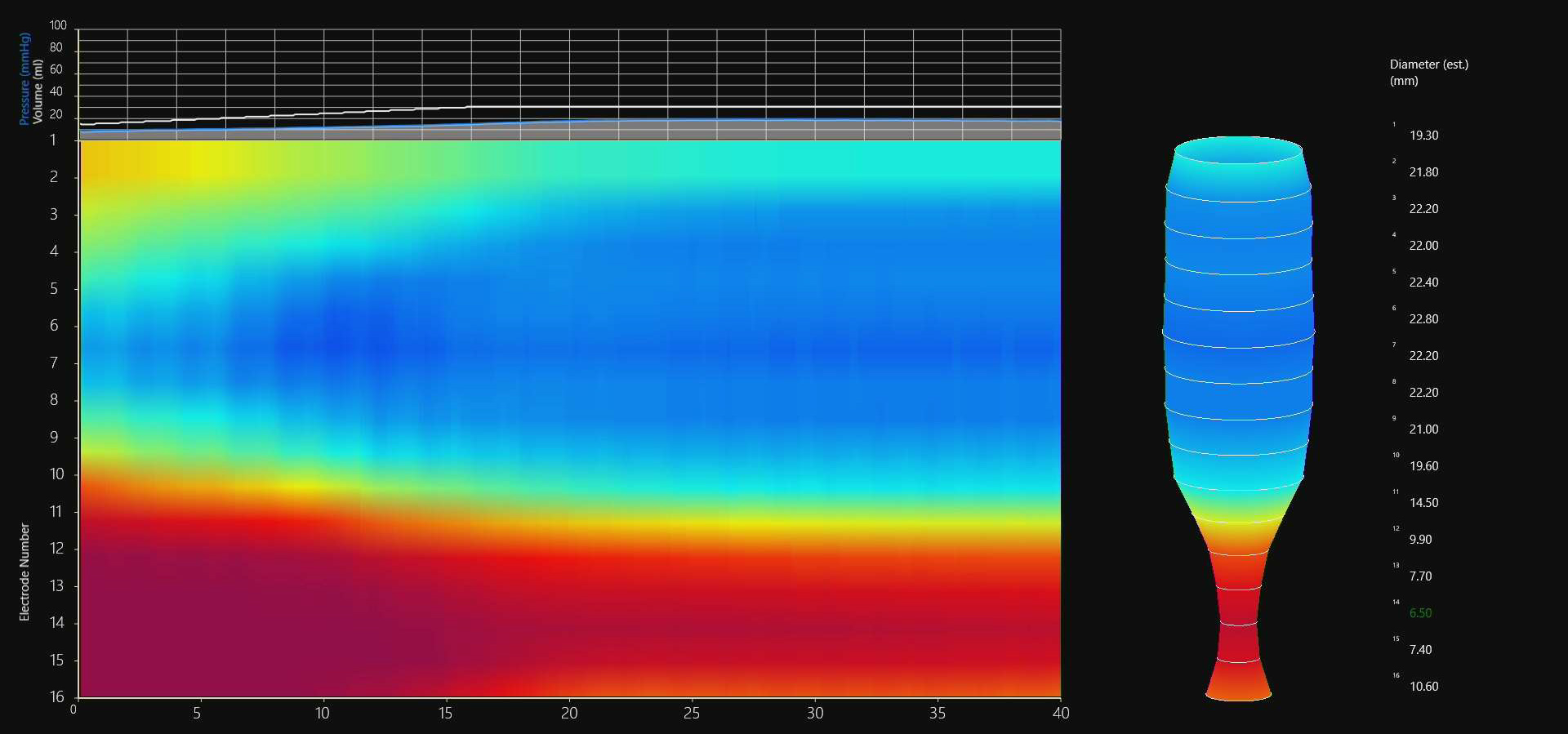
Reflux also known as Gastroesophageal reflux disease (GERD) or acid reflux, is a medical disorder that is characterized by regurgitation of acidic contents of the stomach into the esophagus. There are multiple causes of reflux including hiatal hernia, abnormality of the lower esophageal sphincter, slow emptying of the stomach and abnormal contractions of the esophagus. As a result of reflux the lining of the esophagus may be damaged leading to inflammation, a condition known as esophagitis. Uncomplicated reflux produces symptoms of heartburn, nausea and regurgitation. Reflux may lead to various complications such as Barrett?s esophagus, ulcer and stricture formation of esophagus, asthma, inflammation of the throat and larynx, and lung infection. Various diagnostic tools are used to diagnose reflux including endoscopy, biopsy, X-ray, 24 hour esophageal acid testing, emptying studies of the stomach and motility testing of the esophagus. Reflux is treated using changes in diet and lifestyle, antacids, proton pump inhibitors, H2 blockers, surgery and endoscopy.