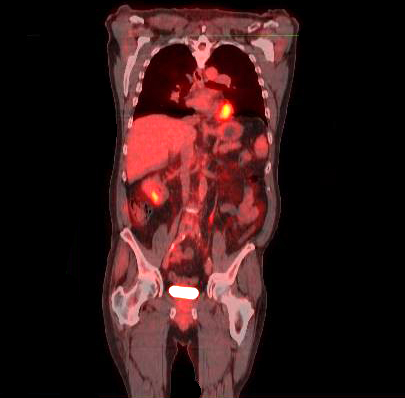
Gene therapy involves the replacement of a disease-causing gene by a healthy gene. The gene is delivered to the target cell carried in a vector. Genetically altered viruses are used as vectors to carry the therapeutic genes. The target cell regains its normal state with the generation of a functional protein product. Gene therapy can be carried out on the somatic cells or the germline cells. A successful gene transplant requires that the gene be transplanted not only into the cell but also be made a part of the chromosome by means of genetic recombination. Cystic fibrosis, hemophilia, and muscular dystrophy are some of the diseases that can potentially be treated with gene therapy.