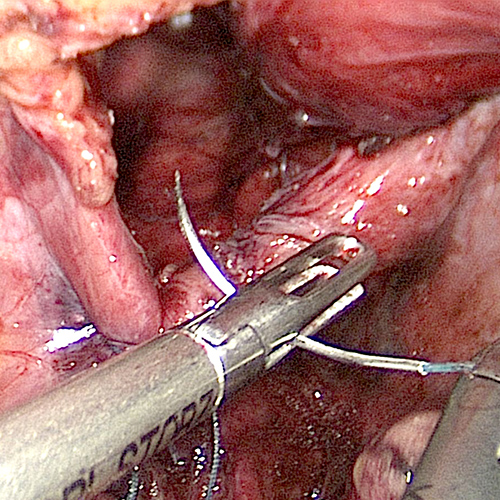
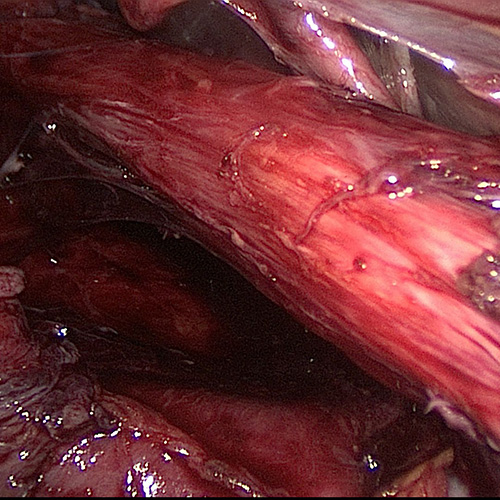
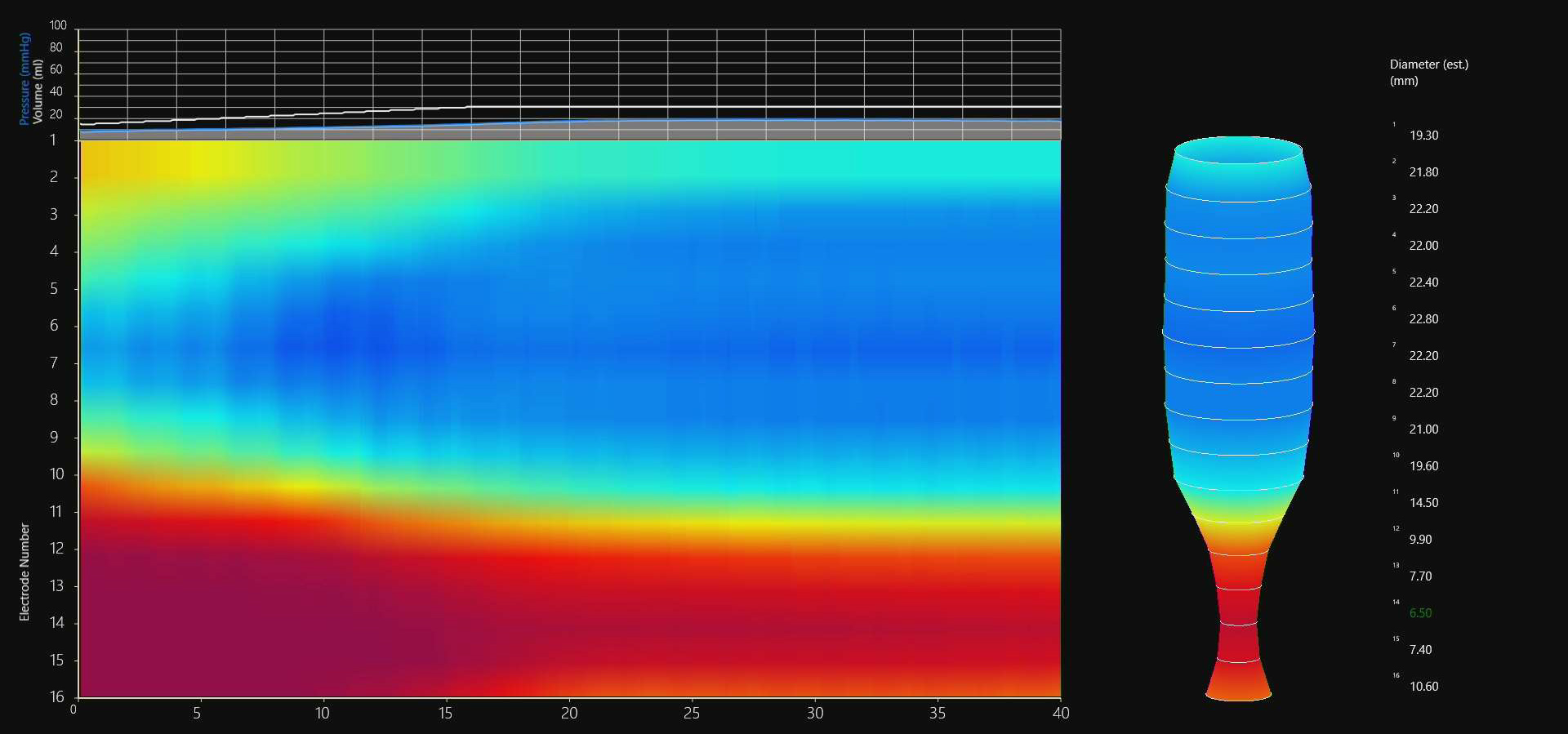
Fundoplication is referred to the surgical procedure that done to treat Gastroesophageal reflux disease (GERD). Under normal circumstances, the reflux of acid from the stomach into the esophagus is prevented by the lower esophageal sphincter, which remains contracted most of the time. In GERD patients the lower esophageal sphincter does not function normally as either its muscles are weak or they remain relaxed. Fundoplication is a surgical procedure that is used to strengthen the lower esophageal sphincter, thereby controlling the reflux of acid from the stomach into the esophagus. During the procedure, the upper part of the stomach (fundus) is gathered and sewed or sutured around the lower esophageal sphincter. The pressure at the lower end of the esophagus is increased after this procedure, thereby, decreasing reflux of acid. If hiatal hernia is also present along with GERD, then the hernia sac is also sutured so that it lies in the abdomen.