The gallbladder concentrates and stores bile as a pear-shaped sac which it can release to help digestion after a fatty meal.
Historically, operating rooms looked more like theaters than modern surgical rooms. They usually consisted of a surgical table placed in the middle of the room with seating available around it, to accommodate medical students and other interested parties. As medicine itself progressed, so did the operating rooms that the staff that work in and the instruments they use. Some operating rooms still have viewing galleries to allow students and medical staff to observe the operation, although the breakthrough operations of today can also be streamed online to different parts of the world.
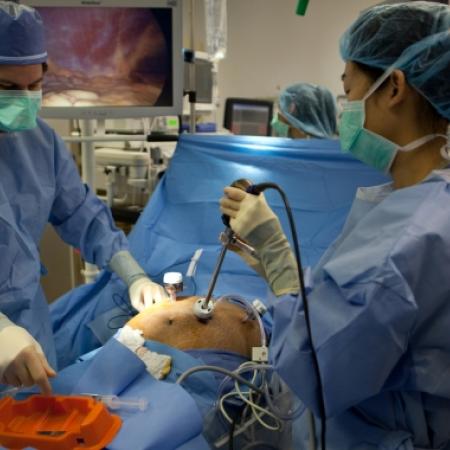
One of the biggest breakthroughs in the operating room comes from the development of modern technology. From small cameras that are inserted into abdomen during laparoscopic surgeries, to robotic systems that are operated by telemanipulation, modern technology has found a strong foothold in the operating room. Take a peek at procedures in the operating room from traditional all the way through the most recently developed technological procedures.