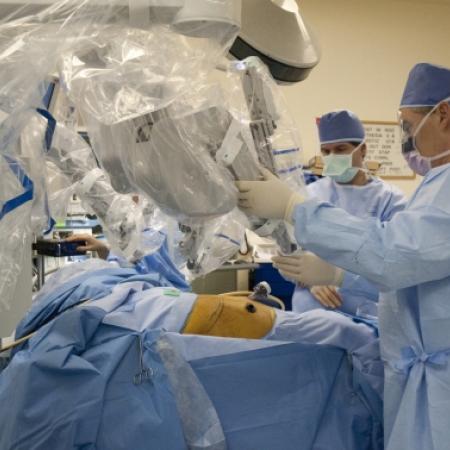
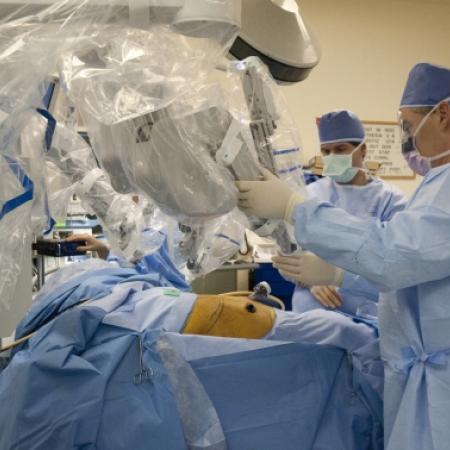
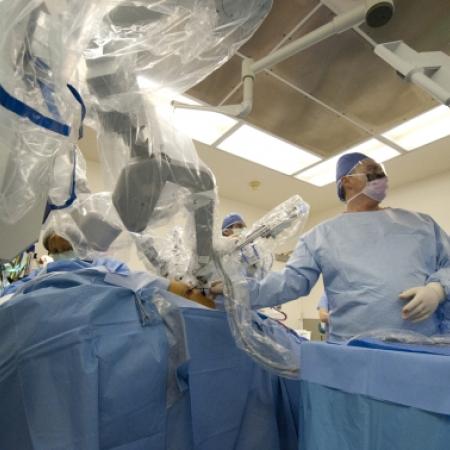
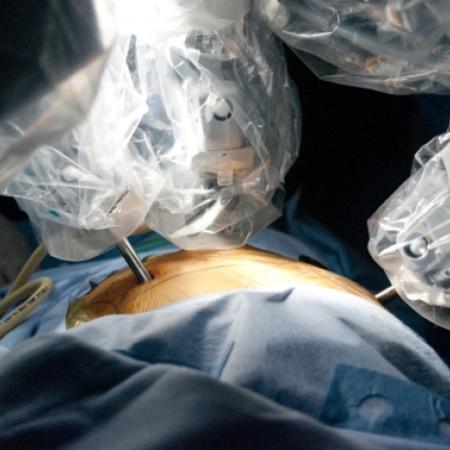
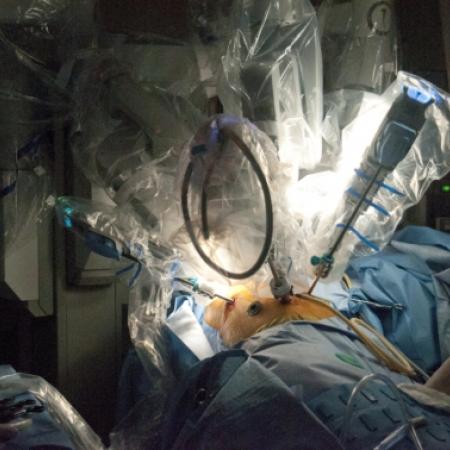
The gallbladder concentrates and stores bile as a pear-shaped sac which it can release to help digestion after a fatty meal.
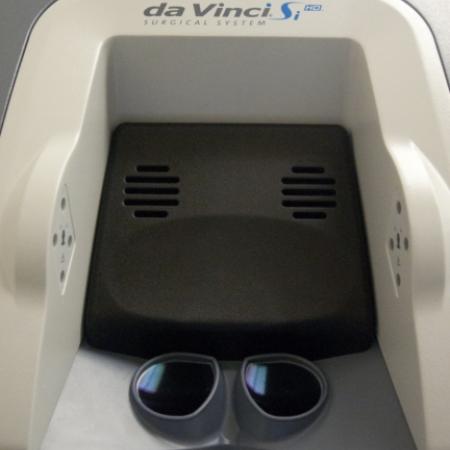
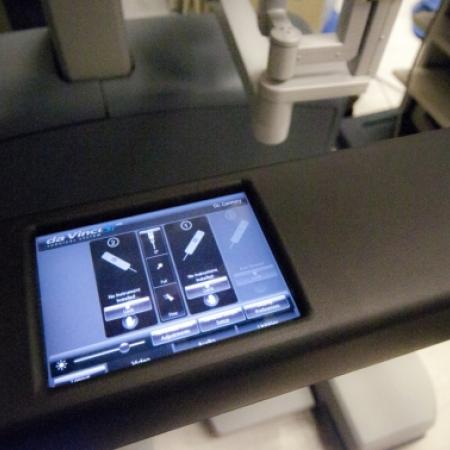
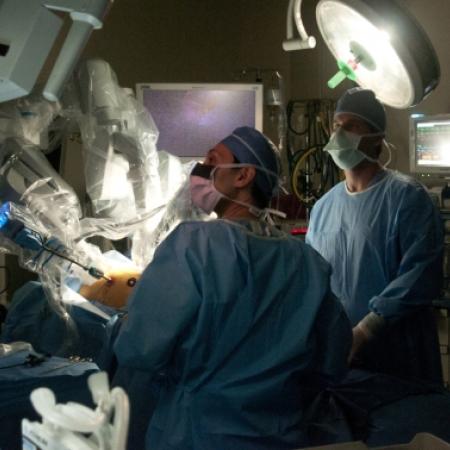
One of the major breakthroughs in the world of surgery is the use of robotics, especially in the field of minimally invasive surgeries. Robotic surgery, computer-assisted surgery and robotically assisted surgery have allowed for increased precision, easier access to the surgical area, and a timelier surgery and recovery period.
The most commonly used surgical robots are operated by telemanipulation, which uses a computer to give the robotic system instructions. Originally, the telesurgery robots were conceived with the help of DARPA and NASA to allow remote surgeries in remote environments, but have since been found more effective for minimally invasive surgeries. Further development of the robotic surgery field is expected to come out of artificial intelligence and miniature robotics research, currently conducted by the leaders in the medical, computer science and defense industries.